本文最后更新于 2025-01-13T17:13:08+08:00
AES基本流程 AES-NI指令集封装好了AES的所有步骤,所以我们没有必要了解每一步的实现方法,只需要了解基本流程就可以了
密钥长度可为128、192、256比特,分别为10轮、12轮、14轮
明文长度都为128比特
在128比特密钥长度中,密钥被拓展成44个四字节数组(uint32_t roundKeys[44]),每轮取4个作为轮密钥
不过我们用SIMD实现,一个元素有16字节大,那就是11个(__m128i roundKeys[11]),每轮取一个作为轮密钥
密钥拓展流程:字循环 -> 字节代换 -> 轮常量异或
加密流程:开始时,进行一次轮密钥加(就是异或运算);之后的每一轮,都是字节替换 -> 行移位 -> 列混合 -> 轮密钥加;最后一轮,进行字节替换 -> 行移位 -> 轮密钥加
注意最后一轮没有列混合,使用的SIMD指令也是不同的(列混合是一个线性变换,它不会增加最后一轮的安全性)
检测CPU是否支持必须的指令集 以下代码获取cpuid并检测是否支持SSE2和AES-NI指令集
只要不是什么老古董大头电脑,都应该支持,除非用户在BIOS里手动关闭了这些功能
参考intel开发手册CPUID—CPU Identification Table 3-19. Feature Information Returned in the ECX Register Table 3-20. More on Feature Information Returned in the EDX Register
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 bool CheckCPUCapability () int i[4 ];1 );bool AES_NI = i[2 ] & (1 << 25 );bool SSE2 = i[3 ] & (1 << 26 );return AES_NI && SSE2;
Unaligned和Aligned指令 Aligned:要求数据内存地址必须对其,可以提升效率,例如MOVDQA指令(_mm_load_si128 _mm_store_si128)
Unaligned:不要求数据对其,例如MOVDQU指令(_mm_loadu_si128 _mm_storeu_si128)
下文中,所有代码都使用Aligned指令
基本SIMD操作 实现AES之前,先来了解一下基本的SIMD操作
我们使用SDK封装好的函数,不需要写汇编,编译器自动帮你隐藏了很多底层细节
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31
实现AES 密钥拓展
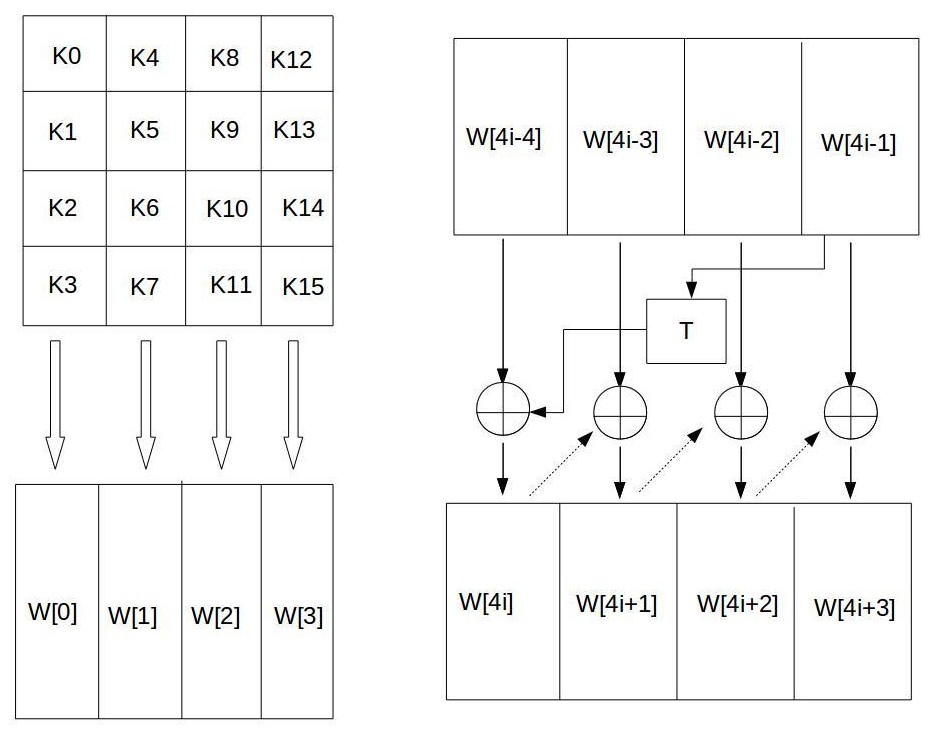
图片来源https://blog.csdn.net/gulang03/article/details/81175854
参考图片可知,本轮的轮密钥由上一轮的轮密钥确定
轮常量Rcon是固定的,为[0x01, 0x02, 0x04, 0x08, 0x10, 0x20, 0x40, 0x80, 0x1B, 0x36]
你问我为什么轮常量是这些数?AES算法又不是我发明的,我哪里知道(笑
第一轮的轮密钥无需计算,直接用_mm_load_si128加载进来便是
后面每一轮i的轮密钥都按以下方式计算
1 2 3 4 W[4 i] = W[4 i-4 ] ⨁ _mm_aeskeygenassist_si128(W[4 i-1 ])4 i+1 ] = W[4 i] ⨁ W[4 i-3 ]4 i+2 ] = W[4 i+1 ] ⨁ W[4 i-2 ]4 i+3 ] = W[4 i+2 ] ⨁ W[4 i-1 ]
举个例子,第二轮的轮密钥为
1 2 3 4 W[4 ] = W[0 ] ⨁ _mm_aeskeygenassist_si128(W[3 ])5 ] = W[1 ] ⨁ W[4 ]6 ] = W[2 ] ⨁ W[5 ]7 ] = W[3 ] ⨁ W[6 ]
上面是伪代码,下面是代码实现:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 static __m128i AES_ExpandKey (__m128i key, __m128i generatedKey) 3 , 3 , 3 , 3 ));4 ));4 ));4 ));return _mm_xor_si128(key, generatedKey);static void AES_GetRoundKeys (uint8_t key[16 ], __m128i roundKey[11 ]) 0 ] = _mm_load_si128((const __m128i*)(key));1 ] = AES_ExpandKey (roundKey[0 ], _mm_aeskeygenassist_si128(roundKey[0 ], 0x01 ));2 ] = AES_ExpandKey (roundKey[1 ], _mm_aeskeygenassist_si128(roundKey[1 ], 0x02 ));3 ] = AES_ExpandKey (roundKey[2 ], _mm_aeskeygenassist_si128(roundKey[2 ], 0x04 ));4 ] = AES_ExpandKey (roundKey[3 ], _mm_aeskeygenassist_si128(roundKey[3 ], 0x08 ));5 ] = AES_ExpandKey (roundKey[4 ], _mm_aeskeygenassist_si128(roundKey[4 ], 0x10 ));6 ] = AES_ExpandKey (roundKey[5 ], _mm_aeskeygenassist_si128(roundKey[5 ], 0x20 ));7 ] = AES_ExpandKey (roundKey[6 ], _mm_aeskeygenassist_si128(roundKey[6 ], 0x40 ));8 ] = AES_ExpandKey (roundKey[7 ], _mm_aeskeygenassist_si128(roundKey[7 ], 0x80 ));9 ] = AES_ExpandKey (roundKey[8 ], _mm_aeskeygenassist_si128(roundKey[8 ], 0x1B ));10 ] = AES_ExpandKey (roundKey[9 ], _mm_aeskeygenassist_si128(roundKey[9 ], 0x36 ));
加解密 轮密钥有了,下面实现加解密函数便可
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 static __m128i AES_Encrypt (__m128i plaintext, __m128i roundKey[11 ]) 0 ]);for (int i = 1 ; i < 10 ; i++)return _mm_aesenclast_si128(plaintext, roundKey[10 ]);static __m128i AES_Decrypt (__m128i cipher, __m128i roundKey[11 ]) 10 ]);for (int i = 9 ; i > 0 ; i--)return _mm_aesdeclast_si128(cipher, roundKey[0 ]);
完整代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 #include <intrin.h> #include <cstdint> static __m128i AES_ExpandKey (__m128i key, __m128i generatedKey) 3 , 3 , 3 , 3 ));4 ));4 ));4 ));return _mm_xor_si128(key, generatedKey);static void AES_GetRoundKeys (uint8_t key[16 ], __m128i roundKey[11 ]) 0 ] = _mm_loadu_si128((const __m128i*)(key));1 ] = AES_ExpandKey (roundKey[0 ], _mm_aeskeygenassist_si128(roundKey[0 ], 0x01 ));2 ] = AES_ExpandKey (roundKey[1 ], _mm_aeskeygenassist_si128(roundKey[1 ], 0x02 ));3 ] = AES_ExpandKey (roundKey[2 ], _mm_aeskeygenassist_si128(roundKey[2 ], 0x04 ));4 ] = AES_ExpandKey (roundKey[3 ], _mm_aeskeygenassist_si128(roundKey[3 ], 0x08 ));5 ] = AES_ExpandKey (roundKey[4 ], _mm_aeskeygenassist_si128(roundKey[4 ], 0x10 ));6 ] = AES_ExpandKey (roundKey[5 ], _mm_aeskeygenassist_si128(roundKey[5 ], 0x20 ));7 ] = AES_ExpandKey (roundKey[6 ], _mm_aeskeygenassist_si128(roundKey[6 ], 0x40 ));8 ] = AES_ExpandKey (roundKey[7 ], _mm_aeskeygenassist_si128(roundKey[7 ], 0x80 ));9 ] = AES_ExpandKey (roundKey[8 ], _mm_aeskeygenassist_si128(roundKey[8 ], 0x1B ));10 ] = AES_ExpandKey (roundKey[9 ], _mm_aeskeygenassist_si128(roundKey[9 ], 0x36 ));static __m128i AES_Encrypt (__m128i plaintext, __m128i roundKey[11 ]) 0 ]);for (int i = 1 ; i < 10 ; i++)return _mm_aesenclast_si128(plaintext, roundKey[10 ]);static __m128i AES_Decrypt (__m128i cipher, __m128i roundKey[11 ]) 10 ]);for (int i = 9 ; i > 0 ; i--)return _mm_aesdeclast_si128(cipher, roundKey[0 ]);int main () uint8_t key[16 ] = { "this is key" };uint8_t plaintext[16 ] = { "plaintext" };uint8_t cipher[16 ] = { 0 };uint8_t decrypted[16 ] = { 0 };11 ];AES_GetRoundKeys (key, roundKey);AES_Encrypt (_mm_loadu_si128((const __m128i*)plaintext), roundKey));AES_Decrypt (_mm_loadu_si128((const __m128i*)cipher), roundKey));
实现操作模式 加密主体写好了,剩下的实现各种操作模式就行了
库:https://github.com/Brassinolide/SIMD-AES
ECB(电子密码本) 最简单的模式,对每个16字节分组都执行相同的加密操作
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 __m128i roundKey[11 ];for (size_t offset = 0 ; offset < cbBufferSize; offset += 16 ) {const __m128i*)(buffer + offset)), roundKey));for (size_t offset = 0 ; offset < cbBufferSize; offset += 16 ) {const __m128i*)(buffer + offset)), roundKey));
CBC(密码分组链接) 初始化向量和第一个明文分组异或后加密,第二个明文分组和第一个密文分组异或后加密,以此类推
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 __m128i roundKey[11 ];const __m128i*)iv);for (size_t offset = 0 ; offset < cbBufferSize; offset += 16 ) {const __m128i*)(buffer + offset))), roundKey);const __m128i*)iv);for (size_t offset = 0 ; offset < cbBufferSize; offset += 16 ) {const __m128i*)(buffer + offset));
CTR(计数器) 加密计数器,再用计数器异或明文
CTR很方便的一点是不需要填充,而且加解密函数完全相同,不需要再编写额外解密代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 __m128i roundKey[11 ];0x00010203 , 0x04050607 , 0x08090a0b , 0x0c0d0e0f );const __m128i*)iv), mask);for (size_t offset = 0 ; offset < cbBufferSize;) {size_t remaining = cbBufferSize - offset;if (cbBufferSize - offset >= 16 ) {const __m128i*)(buffer + offset))));16 ;0 , 1 ));else {uint8_t temp[16 ] = {0 };for (int i = 0 ; i < remaining; i++) temp[i] = buffer[i];const __m128i*)temp)));for (int i = 0 ; i < remaining; i++) buffer[i] = temp[i];break ;
就写到这里吧,剩下的模式懒得实现了,这3种够用(笑